
Challenge
Professor Danielle Manley, Director, Nursing in the Faculty of Science at Carleton University in Ontario, is responsible for creating a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BScN) program, the first new BScN from a university in Ontario in over 20 years. The three-year degree program is scheduled to launch in September 2025. In collaboration with Carleton’s Teaching and Learning Services, she is strategically incorporating AI in the design of the program as well as integrating it into the teaching and learning outcomes, so graduates are proficient in AI’s effective and ethical use.
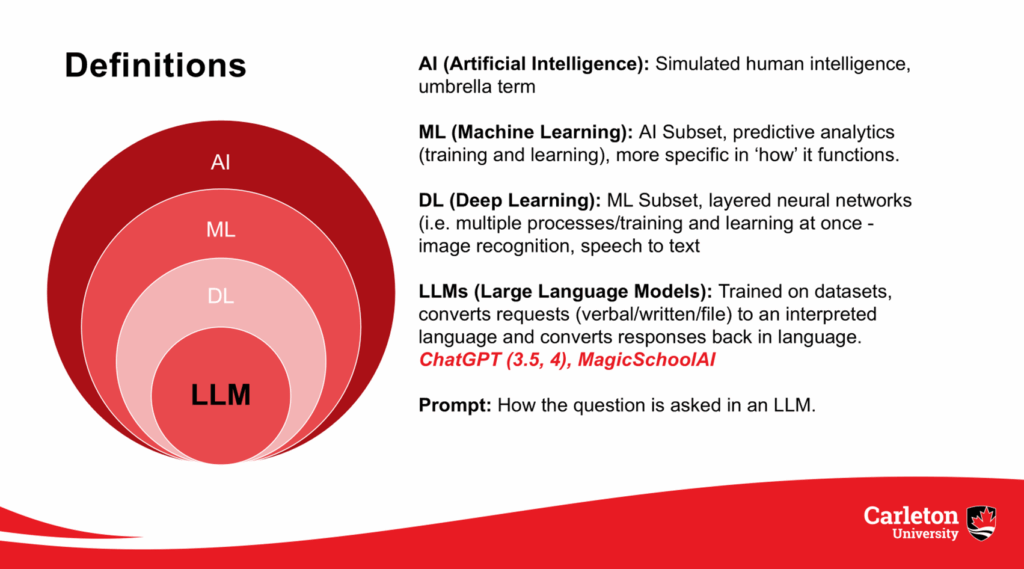
An early adopter of educational technology, Professor Manley is aware that limited understanding of AI terminology can hinder adoption and effective implementation. To address this, she employs a conceptual framework and accompanying diagram to clarify AI’s foundational components:
- Artificial Intelligence: A broad field of computer science focused on creating smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Machine Learning: Training of algorithms to learn from and make decisions based on data.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning that analyzes various factors of data, allowing a system to automatically recognize complex patterns and make intelligent decisions.
- Large Language Models: AI models designed to understand, generate, and interact with human language to perform varied language-based tasks.
- Prompt Engineering: A crucial skill for maximizing AI effectiveness in diverse contexts.
Experimentation and Results
Professor Manley integrates AI as both a tool and a partner in the iterative process of the degree program development – prompting, reviewing, re-prompting and evaluating output continuously. She selectively accepts, revises and discards AI-generated material based on its quality, relevance, utility and accuracy.
Two large language models (LLMs) were central to her work – ChatGPT and MagicSchool.ai.
ChatGPT proved especially effective for broad spectrum research, while MagicSchool.ai – developed by educators for educators – offers over 80 tools for curriculum development, assessment, and academic and student support.
Over 18 months, the BScN development process spanned proposal writing, curriculum design, specialization definition, resource planning, as well as the creation of learning objectives, course outlines, assessments and rubrics. Each stage builds on prior work and many are subject to official review and approval.
Review of Existing Programs: One of Professor Manley’s first initiatives was instructing ChatGPT to examine what other universities include in their three-year undergraduate degree nursing programs. Through precise prompts and rigorous fact checking, she conducted a comprehensive scan of objectives, content, and other key factors in existing programs.
Specializations: In defining the two proposed concentrations – Data Science and Mental Health – she prompted ChatGPT to search for similar specializations in existing programs. In the emerging field of data science in health care provision, she not only found relevant material but also established a connection with another institution with the same focus.
Curriculum: As the core tool for developing all aspects of the program, Professor Manley created a personalized, custom version of ChatGPT linking to the sites essential for nursing education in Ontario and Canada. These include the Entry to Practice Competencies established by the College of Nurses of Ontario (CNO) which guides program alignment and approval in Ontario Undergraduate Nursing Programs. Since nursing students must meet all these standards to graduate, they are the essential foundation for curriculum development. Additional guidance came from the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario (RNAO), the Canadian Association of Schools of Nursing (CASN), the Canadian Nurses Association (CNA), as well as Carleton University guidelines and guidance on the integration of Indigenous knowledge systems. Her Custom ChatGPT prioritized the content of these sources before conducting broader research to respond to her request to outline essential curriculum components.
By integrating ChatGPT access to the Universal Instructional Design (UDL) Principles to promote inclusive and equitable access to learning, she was able to prompt AI to make suggestions and provide examples on how to apply UDL Principles throughout the curriculum.
Financial Model: To develop a financial model for the new program, she shared program cost components with ChatGPT, asking it to make a return on investment investigation of expenses at other institutions. She described this process as using AI as a Socratic Opponent, with structured questions and answers to further explore and understand comparative expenses. Using this information, she aligned projected expenses with the experiences and requirements of other universities.
Program and Course Learning Objectives: Professor Manley used MagicSchool.ai to create learning objectives, first for the program and then for individual courses. Based on the curriculum content she developed, she prompted it to outline potential learning objectives in a continual process of questions, responses and reviews. MagicSchool.ai also requested information on several factors such as students’ level of education/preparation and levels of learning to be achieved.
Course Outlines: When the learning objectives were approved, Professor Manley began course preparation in her own areas of specialization – Professional Practice and Data Science. Subject matter experts work from the course learning objectives and other curriculum materials she prepared to develop other courses, such as Pediatrics and Critical Care. She put a course outline sample and standards on the learning management system (LMS) to ensure consistency in course development and supports colleagues in their course design.
Class Content and Hours: Once again using ChatGPT, Professor Manley provided the entry requirements for the nursing profession as outlined by the professional associations and asked it to group them together into competencies. She then started a detailed dialogue with ChatGPT, asking it to link the competencies to her course learning objectives and provide alternatives on how this essential learning could best be addressed in each course – sequencing of content, how many weeks of teaching, how many class hours per week, and credit weighting – benchmarked against similar programs. Once she was satisfied with the quality and detail of the AI responses, she manually created the classes.
Assessments and Rubrics: Using the course learning objectives and the class content and structures, she asked MagicSchool.ai to outline possible mid-term and final exams or assignments, suggesting grade weight and other activities and assignments for each class. Once she chose the assignments, she requested grading rubrics for the students. Among other factors, the rubrics make clear what uses of AI are permitted in completing assignments and activities. The result of this extensive interaction was the outline of weekly topics and activities, matched with assignments and rubrics.
Role of AI: Professor Manley stresses that AI is an effective and time-saving partner that needs to be monitored, assessed and revised continuously. It should never be accepted as a final source without verification. It made possible detailed research and analyses, such as that on other universities’ three-year programs, which would have been more time-consuming and far less comprehensive without AI. It played an essential role in each of the tasks outlined above.
AI also helped translate technical, discipline-specific language into more accessible phrasing for non-specialist review committees, enhancing communication across institutional stakeholders.
Next Development Steps
The Data Science specialization comprises six required courses distributed over the program’s three years. The first two, Data Management and Advanced Analytics, will be offered in 2026. The third course will focus on the evaluation and procurement of and project management of technologies in health care. Ethics, legalities and regulation of AI will be offered later in the program. Professor Manley expects the AI environment to change drastically and wants graduates to be as up-to-date as possible on these critical factors when they complete their training. Two tutorial classes are not yet defined, as they will be developed in the future to reflect AI realities in 2028 and 2029.
Professor Manley considers ethics to be a key consideration for the use of AI in healthcare. She plans to use her customized ChatGPT, with its content links to the nursing associations, to illustrate the biases possible with AI. In class, she and the students will research questions starting with professional basics like “What is a Professional Nurse?” and moving on to more sophisticated questions accessing research data and other sources. She will share the answers from her custom ChatGPT and compare them with what students receive from the free version of ChatGPT. The biases built into the research become evident when comparing the results. Revealed discrepancies form the basis for planned critical, reflective inquiry in class.
Potential
To graduate, BScN students must pass the National Council Licensure Examination, an adaptive, AI-generated test with thousands of questions ranked by difficulty. The student advances through levels of questions of increasing difficulty until they reach their highest, consistent level, passing if this is above the required level. This test creates high levels of anxiety for the students.
To support students, Carleton will be partnering with the publisher Elsevier to develop AI-based practice tests using the required textbooks, giving students early exposure to exam conditions and requirements.
The goal of the Data Science specialty within Carleton University’s Bachelor of Science in Nursing program is for the graduates to be at the forefront of technology and data science, equipped to bridge the gap between technical skills and clinical experience. Their advanced knowledge can drive innovation in data science, artificial intelligence and healthcare.
The Data Science concentration in the BScN program will be taught at Carleton’s location at Kanata North, a centre of technological innovation where students can benefit from proximity to leading experts and industry developments.
For Further Information

Danielle Manley
Director, Nursing
Department of Science
Carleton University
Ottawa, Ontario